Week 2, Day 1: File Systems
CMPSC 100 Computational Expression
File Systems
File systems organize data in a tree-like structure
File Systems are Hierarchical
- Folders (also called directories) can contain:
- Files (documents, images, code, etc.)
- Other folders (creating nested structure)
- Think of it like boxes that hold objects and other boxes
- Two ways to visualize the same file system:
Parents, Children, Siblings
Family relationships describe folder connections:
- Parent: The folder that contains other folders
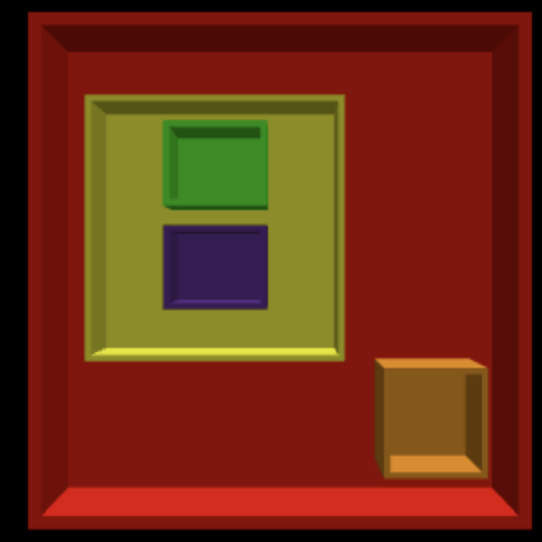
redis the parent ofyellowandorange
- Children: Folders contained within a parent folder
greenandpurpleare children ofyellow
- Siblings: Folders that share the same parent
yellowandorangeare siblingsgreenandpurpleare siblings
Directories
Directory = Folder (same thing!)
- Different operating systems use different terms:
- Windows: “Folder”
- Mac/Linux: “Directory”
- Programming: Often “Directory”
- Contains files and other directories
- Organizes your digital workspace
Root Directory
The root directory contains everything else:
- Root: The top-level folder in the file system
- Contains all other directories and files
- In our example:
redis the root directory - Important: Every file system has exactly one root directory
File Paths
A path shows the route to a specific file or folder:
- Path: The full address from root to your target
- Always starts at the root directory
- Gets more specific as you go deeper
- Uses
/(forward slash) to separate folders
Examples from our tree:
- Path to
purple:red/yellow/purple - Path to
orange:red/orange - Path to
green:red/yellow/green
Navigating File Systems
Two main ways to explore your files:
- Graphical File Explorer:
- Windows: File Explorer
- Mac: Finder
- Linux: Files/Nautilus
- Click and visual navigation
- Terminal/Command Line:
- Text-based navigation
- More powerful and precise
- We’ll use this in class!
Important: Be careful with cloud storage - files might not be locally stored!
Using the Terminal
Opening Terminal in VS Code
VS Code has a built-in terminal - perfect for our work!
- Keyboard shortcut:
- Windows/Linux: `Ctrl + `` (backtick)
- Mac: `Cmd + `` (backtick)
- Menu: View → Terminal
- Command Palette:
Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + P→ “Terminal: Create New Terminal”
Benefits:
- Integrated with your code editor
- Same directory as your project
- Easy to switch between coding and terminal commands
What is the Terminal?
The terminal is a text-based interface to your computer:
- Also called: Command line, shell, console
- No mouse needed - everything done with keyboard
- More powerful than graphical interfaces
- Faster once you learn the commands
- Essential skill for programming and development
Why use terminal?
- Automation and scripting
- Precise control over files and folders
- Works on all operating systems
- Many development tools are terminal-based
Terminal Basics
Key commands for navigation:
pwd- Print Working Directory (where am I?)ls- List files and folderscd- Change Directory
Basic Navigation Commands
Essential commands for moving around:
List contents:
- Shows files and folders
ls -lfor detailed viewls -ato show hidden files
Change directory:
- Moves into a folder
- Must spell folder name exactly
Creating and Managing Folders
Making new directories:
Examples:
Best practices:
- Use descriptive names
- Avoid spaces (use underscore or dash)
- Use lowercase for consistency
- Examples:
cmpsc100_f2025,lab1
More Useful Commands
File and directory operations:
Special Directory Shortcuts
Helpful shortcuts to remember:
.(dot) = Current directory..(dot dot) = Parent directory
~(tilde) = Home directory/(forward slash) = Root directory
Examples:
Terminal Practice Tips
Getting comfortable with the terminal:
- Start small: Practice with simple commands
- Use tab completion: Type first few letters, press Tab
- Arrow keys: Up/down to recall previous commands
- Clear screen:
clearcommand orCtrl+L - Don’t be afraid: You can always navigate back!
Safety tips:
- Be careful with
rm(delete) commands - Use
lsto check contents before moving - Practice in a safe folder first
